Product Description
Professional CNC Machining Parts Supplier-HangZhou XINGXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.NG PRECISION INDUSTRY CO.,LTD.-Focus on & Professional
| Material: | Aluminum (6061-T6, 6063, 7075-T6,5052) etc… |
| Brass/Copper/Bronze etc… | |
| Stainless Steel (201, 302, 303, 304, 316, 420, 430) etc… | |
| Steel (mild steel, Q235, 20#, 45#) etc… | |
| Plastic (ABS, Delrin, PP, PE, PC, Acrylic) etc… | |
| Process: | CNC Machining, turning,milling, lathe machining, boring, grinding, drilling etc… |
| Surface treatment: | Clear/color anodized; Hard anodized; Powder-coating;Sand-blasting; Painting; |
| Nickel plating; Chrome plating; Zinc plating; Silver/gold plating; | |
| Black oxide coating, Polishing etc… | |
| Gerenal Tolerance:(+/-mm) | CNC Machining: 0.005 |
| Turning: 0.005 | |
| Grinding(Flatness/in2): 0.005 | |
| ID/OD Grinding: 0.002 | |
| Wire-Cutting: 0.003 | |
| Certification: | ISO9001:2008 |
| Experience: | 15 years of CNC machining products |
| Packaging : | Standard: carton with plastic bag protecting |
| For large quantity: pallet or as required | |
| Lead time : | In general:15-30days |
| Term of Payment: | T/T, Paypal, Western Union, L/C, etc |
| Minimum Order: | Comply with customer’s demand |
| Delivery way: | Express(DHL,Fedex, UPS,TNT,EMS), By Sea, By air, or as required |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Fastener, Auto and Motorcycle Accessory, Hardware Tool, Machinery Accessory |
|---|---|
| Standard: | GB, EN, API650, China GB Code, JIS Code, TEMA, ASME |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Production Type: | Mass Production |
| Machining Method: | CNC Machining |
| Material: | Nylon, Steel, Plastic, Brass, Alloy, Copper, Aluminum, Iron |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How are sprocket pulleys customized for specific applications and load requirements?
Sprocket pulleys can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different applications and load conditions. Here’s an explanation of how customization is achieved:
1. Size and Diameter: Sprocket pulleys are available in various sizes and diameters to accommodate different application requirements. The selection of the appropriate size and diameter depends on factors such as the available space, desired speed ratio, and torque transmission capabilities. Larger pulleys are typically used for applications that require higher torque transmission, while smaller pulleys are suitable for applications with limited space or lower load requirements.
2. Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on a sprocket pulley can be customized based on the desired speed ratio and load distribution. Pulleys with more teeth provide finer speed adjustments and distribute the load across a larger number of contact points, reducing wear and increasing load capacity. Conversely, pulleys with fewer teeth offer a coarser speed ratio but may be suitable for applications with limited space or specific torque requirements.
3. Material Selection: The choice of material for sprocket pulleys depends on factors such as the application environment, load requirements, and desired durability. Common materials used for sprocket pulleys include steel, cast iron, aluminum, and plastics. Steel and cast iron pulleys are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Aluminum pulleys are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, often used in applications where weight reduction is important. Plastic pulleys are lightweight, economical, and can provide quieter operation.
4. Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of sprocket pulleys can be customized to match the corresponding chain type. Different chain types, such as ANSI, ISO, or specialty chains, have specific tooth profiles that ensure proper engagement and smooth operation. Customizing the tooth profile allows for compatibility and optimized performance between the sprocket pulley and the chain.
5. Coating and Surface Treatment: Sprocket pulleys can be coated or surface-treated to enhance their performance in specific applications. Coatings such as zinc plating, black oxide, or corrosion-resistant coatings can improve the pulley’s resistance to wear, rust, and environmental conditions. Surface treatments like heat treatment or induction hardening can increase the hardness and wear resistance of the pulley teeth, prolonging their lifespan in demanding applications.
6. Special Features: Depending on the application requirements, sprocket pulleys can be customized with special features. These features may include timing marks, keyways, set screws, hubs, or flanges to facilitate precise positioning, mounting, or connection with other components in the system.
7. Engineering Support: Customization of sprocket pulleys often involves engineering support to ensure that the pulley design meets the specific application and load requirements. Manufacturers or suppliers can provide assistance in selecting the appropriate pulley specifications, considering factors such as load capacity, speed, torque, and environmental conditions.
By offering customization options in terms of size, diameter, number of teeth, material selection, tooth profile, coating, surface treatment, and special features, sprocket pulleys can be tailored to meet the unique demands of various applications and load requirements.
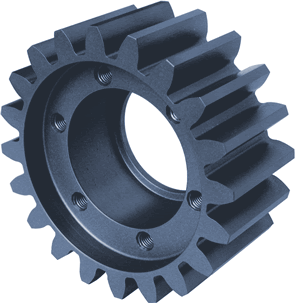
How do you select the right sprocket pulley configuration for a particular machinery or system?
Selecting the appropriate sprocket pulley configuration for a specific machinery or system involves considering several factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to make the right selection:
1. Determine Power Requirements: Start by determining the power requirements of the machinery or system. This includes identifying the input power source, such as an electric motor or an engine, and understanding the required output power and torque. Consider factors such as load characteristics, operating conditions, and desired performance parameters.
2. Calculate Speed Ratio: Calculate the required speed ratio between the driving source and the driven component. The speed ratio is determined by the desired rotational speed of the driven component relative to the driving source. It influences the number of teeth on the sprocket pulleys and the chain pitch required for the drive system.
3. Assess Space Limitations: Evaluate the available space and layout constraints within the machinery or system. Consider factors such as the distance between the driving source and the driven component, the size of the sprocket pulleys, and any clearance requirements. Ensure that the selected sprocket pulley configuration can fit within the given space without interference.
4. Consider Load Capacity: Determine the load capacity requirements of the machinery or system. This involves assessing the forces and torques that will be transmitted through the sprocket pulleys and the chain. Consider factors such as the weight of the load, dynamic loads, and any potential shock or impact loads. Select sprocket pulleys that can handle the anticipated load capacity without excessive wear or failure.
5. Choose Material and Tooth Profile: Select the appropriate material and tooth profile for the sprocket pulleys based on the application requirements. Consider factors such as the operating environment (e.g., temperature, moisture, chemicals), the desired durability, and the type of chain being used. Common materials for sprocket pulleys include steel and cast iron, while tooth profiles may vary depending on the specific chain type (e.g., ANSI standard, British standard).
6. Consult Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines, specifications, and recommendations for sprocket pulley selection. Manufacturers often provide detailed catalogs or online tools that assist in choosing the appropriate sprocket pulley configuration based on application parameters. These resources provide valuable information regarding load capacities, speed ratios, dimensions, and other relevant considerations.
7. Consider Maintenance and Replacement: Evaluate the ease of maintenance and replacement for the selected sprocket pulley configuration. Factors such as accessibility, hub design (e.g., split hubs, taper-lock), and availability of replacement parts should be taken into account to ensure smooth maintenance procedures and minimize downtime.
By carefully considering power requirements, speed ratio, space limitations, load capacity, material selection, manufacturer’s guidelines, and maintenance aspects, you can select the right sprocket pulley configuration that meets the specific needs of your machinery or system.

How does the design of sprocket pulleys contribute to precise motion control in systems?
The design of sprocket pulleys plays a crucial role in contributing to precise motion control in systems. Here’s an explanation of how the design of sprocket pulleys enables precise motion control:
1. Toothed Surface: Unlike traditional pulleys, sprocket pulleys have a toothed surface with teeth or cogs arranged around the outer circumference. These teeth mesh with the links of a chain or timing belt, creating a positive engagement. The toothed surface ensures a secure connection between the pulley and the chain or belt, preventing slippage and ensuring precise motion control.
2. Accurate Positioning: The teeth on the sprocket pulley allow for accurate positioning of the connected components. As the chain or timing belt moves along the teeth, the position of the driven component can be precisely controlled. This is particularly important in applications where precise positioning is crucial, such as robotics, automated manufacturing, and printing presses.
3. Smooth and Consistent Motion: The toothed design of sprocket pulleys contributes to smooth and consistent motion control. The engagement between the teeth and the chain or timing belt helps to minimize vibrations, jerks, and fluctuations in speed. This promotes stable and predictable motion, which is essential for applications that require precise control over the movement of components.
4. Reduced Backlash: Backlash refers to the slight movement or play between the driving and driven components when the direction of motion is reversed. Sprocket pulleys, with their toothed design, help reduce backlash. The teeth ensure a positive engagement with the chain or timing belt, eliminating or minimizing any free play and providing more accurate and responsive motion control.
5. High Torque Transmission: Sprocket pulleys are capable of transmitting high levels of torque efficiently. The toothed design allows for a larger contact area between the pulley and the chain or belt, distributing the torque more evenly. This enables the sprocket pulley to handle higher loads and deliver precise motion control even in applications that require significant power transmission.
6. Timing and Synchronization: Sprocket pulleys, in conjunction with timing belts, facilitate precise timing and synchronization of components in systems. The teeth on the pulley and the corresponding teeth on the timing belt ensure accurate coordination of the movement between multiple pulleys, enabling precise control over the timing of events or the synchronized operation of various parts.
7. Multiple Teeth Engagement: Sprocket pulleys typically have multiple teeth engaged with the chain or timing belt at any given time. This multi-tooth engagement provides more contact points and distributes the load across the teeth, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of both the pulley and the chain or belt. It also contributes to smoother and more precise motion control.
Overall, the toothed design of sprocket pulleys, with its secure engagement, accurate positioning, smooth motion, reduced backlash, high torque transmission, timing and synchronization capabilities, and multiple teeth engagement, ensures precise motion control in systems. These design features make sprocket pulleys suitable for applications where accurate and reliable motion control is essential.


editor by CX
2024-05-07
